Surgical Shadowless Lamp: Illuminating the Light of Hope for Life
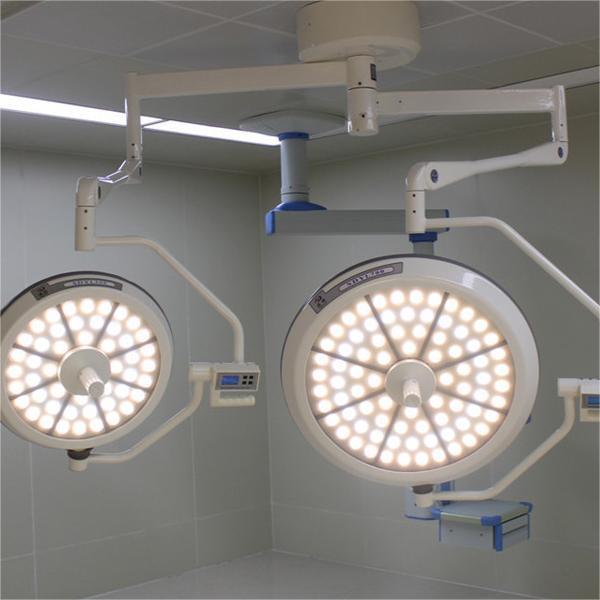
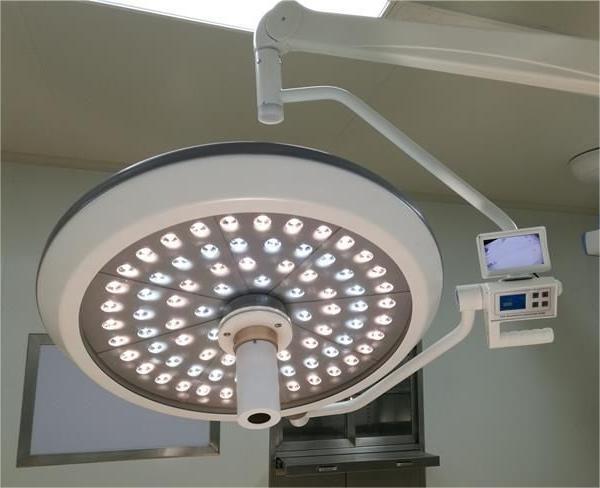
In modern medical surgery, the shadowless lamp is an indispensable device that provides crucial lighting conditions for the smooth progress of the surgery.
Surgical shadowless lamps are widely used in various surgical scenes. It can be seen in large and complex surgeries such as heart bypass and brain tumor resection, as well as routine surgeries such as fracture reduction and ordinary debridement and suturing. In cardiac surgery, doctors need to precisely suture blood vessels, and shadowless lamps ensure that every subtle structure of the heart is clearly visible, allowing doctors to perform delicate operations on extremely small blood vessels. In ophthalmic surgery, doctors need to repair the extremely small tissues inside the eyeball. The high-quality lighting provided by shadowless lamps enables doctors to clearly distinguish fine structures such as the retina and lens, ensuring the accuracy of the surgery.
Surgical shadowless lamps have numerous significant advantages. Firstly, the absence of shadows is its key characteristic. Traditional single light source illumination can produce significant shadows, affecting doctors’ comprehensive observation of the surgical site. The shadowless lamp combines multiple light sources to project light from different angles, complementing each other and effectively eliminating shadows in the surgical area. Even if the doctor’s head, hands, or instruments obstruct some of the light, other surrounding light sources can still illuminate the area, allowing the doctor to always see all aspects of the surgical site clearly, avoiding visual blind spots caused by shadows and improving surgical safety.
Secondly, the illumination of the surgical shadowless lamp is extremely high and adjustable. Generally speaking, its illumination can reach tens of thousands of lux, far higher than ordinary ambient lighting. This high-intensity lighting can clearly display the tissue structure, vascular distribution, and other details of the surgical site. At the same time, doctors can flexibly adjust the light intensity according to actual needs such as surgical type and depth of the site. For example, in superficial surgery, reducing the light intensity appropriately can reduce irritation to the patient’s eyes and other parts; In deep tissue surgery, enhancing light intensity is necessary to see deep structures clearly.
Furthermore, the color temperature of the surgical shadowless lamp is close to natural sunlight, usually between 4000K and 5000K. This suitable color temperature allows doctors to see tissue colors that are closer to reality, accurately determining the health status of the tissue, blood color, and so on. For example, accurate color recognition can help doctors determine the resection range more accurately when judging the tumor boundary, avoiding the accidental cutting of normal tissue or residual lesion tissue.
In addition, the surgical shadowless lamp also has good heat dissipation performance. Long term illumination during surgery can generate heat. If it is not dissipated in a timely manner, it not only affects the lifespan of the light bulb but may also cause thermal damage to the surgical site. The advanced heat dissipation design enables the shadowless lamp to efficiently dissipate heat, maintain a suitable temperature, and ensure safe surgical procedures.
Post time: Mar-10-2025