Geomembrane: a multifunctional material with excellent performance
Geomembranes are made from synthetic polymer materials through special processes and are widely used in many fields.
Building a versatile foundation with outstanding features
1. Excellent impermeability: The geomembrane structure is dense and extremely difficult for liquids to penetrate. The permeability coefficient of HDPE geomembrane is often lower than 10 ⁻¹² cm/s, effectively blocking water and other liquid leakage, and is indispensable in projects with high anti-seepage requirements such as water conservancy and environmental protection.
2. Good chemical stability: It can resist the erosion of various chemical substances, whether it is industrial wastewater with strong acids and alkalis, or soil environments rich in various salts, it is difficult to cause damage to it. It is suitable for engineering in complex chemical environments such as chemical engineering and landfill.
3. Excellent weather resistance: Geomembranes have stable performance under different climatic conditions. It will not soften or deform at high temperatures, and will not crack at low temperatures. It can function normally in both hot deserts and cold polar regions.
4. High mechanical strength: It has good tensile strength and tear strength, and can withstand the action of various construction equipment during the laying process without being easily damaged; During use, it can also withstand certain external loads to ensure long-term stable operation of the project.
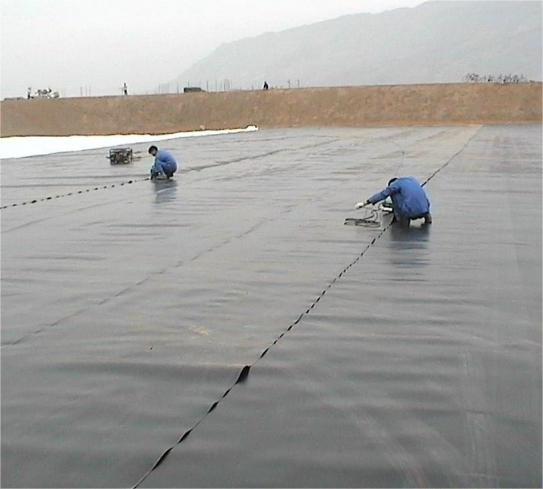
5. Convenient construction: Relatively lightweight, easy to transport and lay on site. There are various and convenient connection methods, such as welding, bonding, etc., which can quickly form a continuous anti-seepage layer, improve construction efficiency, and ensure the sealing of the connection part.
6. Significant cost-effectiveness: Long service life, up to 50 years or even longer, reducing the cost and hassle of frequent material replacement. Taking into account the long-term effectiveness, the cost-effectiveness advantage is obvious.
Diversified applications support the development of various fields
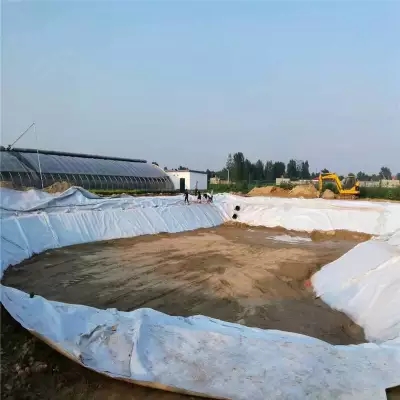
1. Water conservancy engineering: In reservoir construction, geomembranes are laid at the bottom and dam body to effectively reduce leakage, improve water resource utilization, and enhance reservoir stability; Geomembranes are used for channel anti-seepage to reduce water loss during water transmission and ensure irrigation water demand.
2. Environmental protection engineering: Geomembranes are laid at the bottom and walls of landfills to form anti-seepage barriers and prevent soil and groundwater pollution caused by leachate from garbage; Geomembranes are used in the water tanks, regulating tanks, etc. of sewage treatment plants to prevent sewage leakage from polluting the surrounding environment.
3. Mining engineering: The anti-seepage treatment of tailings ponds is crucial. Geomembranes can prevent harmful substances such as heavy metals from seeping out of tailings, avoiding serious pollution to surrounding soil and water bodies.
4. In the field of agriculture, the use of geomembranes in artificial lakes and aquaculture ponds can maintain water levels, reduce water evaporation and leakage, and create a favorable water environment for aquaculture; In irrigation systems, it can prevent water resource waste and improve irrigation efficiency.
5. Transportation engineering: In road construction, geomembranes can be used for roadbed seepage prevention to prevent groundwater from rising and causing damage to the roadbed, thereby extending the service life of the road; In tunnel engineering, geomembranes can play a waterproof and moisture-proof role, protecting the internal structure of the tunnel from water erosion.
Post time: Mar-27-2025