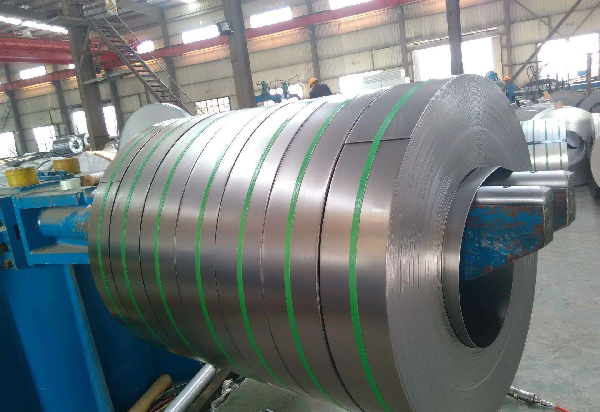
Galvanized products are ubiquitous in our lives. All steel processing products with corrosion resistance requirements, including corrugated plates used as building materials, automotive sheet metal used as car facades, daily open refrigerators, as well as high-end computer server casings, furniture, colored substrates, slides, air ducts, etc., can be processed using hot-dip galvanized steel coils.
For example, the shells of some advanced computers and servers are not painted, but are directly exposed with galvanized steel plates. For these manufacturers, they will need a thin layer of zinc coating to maintain the beautiful surface quality of their products. Relatively speaking, manufacturers of corrugated building materials have lower requirements for the surface quality of steel coils. Considering that the waveform board may be installed in areas with poor environmental conditions, they will use a thicker zinc layer to manufacture products with high corrosion resistance.
Due to the different thicknesses of galvanized molds required by different customers, accurately controlling the thickness of the zinc layer has become the main challenge faced by Zhongshen hot-dip galvanizing plants.
Different products have different galvanized film thicknesses. If there is too much galvanizing, exceeding the thickness required by the customer, zinc is one of the higher cost raw materials, which will cause cost waste; If the galvanized layer does not meet the product specifications, it will result in customer inability to use or subsequent processing problems, leading to customer complaints about quality.
If one sentence is used to explain the hot-dip galvanizing method, it is to put the steel coil into a zinc bath, so that both sides of the steel coil are coated with zinc liquid, so as to attach a thin layer of zinc on the surface of the steel plate, which can resist corrosion. However, in fact, to produce several tons of hot-dip galvanized steel coils, a series of complex processing processes are required, which sequentially enter the feeding area, annealing area, galvanizing area, tempering and leveling area, coating area, inspection area, and unloading area to complete the hot-dip galvanizing work.
Post time: May-10-2024