1. Used to stabilize railway subgrade;
Paved on railway subgrade, it increases the overall strength of the subgrade, prolongs its service life, reduces daily maintenance and repair costs, and significantly reduces the occurrence of faults during train operation, ensuring the safe operation of trains. It is widely used in current railway construction.

2. Used to stabilize the roadbed of highways;
This effect is equivalent to the application of railway subgrade, which can significantly reduce the stress splitting reflected by the subgrade on the road surface. The subgrade does not crack, and the road surface naturally does not crack, especially in northern urban roads with warm winter and cool summer and large temperature differences. In winter, asphalt pavement cracks severely. Strengthening the subgrade with geogrids is very effective.
3. Embankments and retaining walls used to withstand heavy loads;
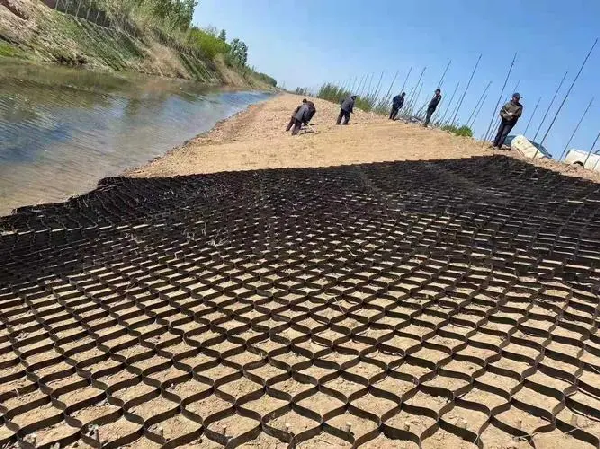
The two slopes of the river and the walls with a large inclination angle are both specific engineering projects that use geogrids. Especially for river slopes that have been in a humid environment for a long time, they are prone to collapse in rainy and snowy weather. By using the honeycomb structure of geogrids, the soil at the inclination angle can be fixed.
4. Used for shallow water channel management;
This application is also increasing.

5. Used to support pipelines and sewers;
Can increase overall stress resistance.
6. A hybrid retaining wall designed to prevent landslides due to its load-bearing gravity;
Equivalent to the effect of Article 3.
7. Used for independent walls, docks, breakwaters, etc;
It can replace geogrids because geogrids are three-dimensional structures, while geogrids are planar structures.
8. Used for desert, beach, riverbed, and riverbank management.
This effect is obvious, as it has been widely used in desert areas for many years.
Post time: Jun-19-2024