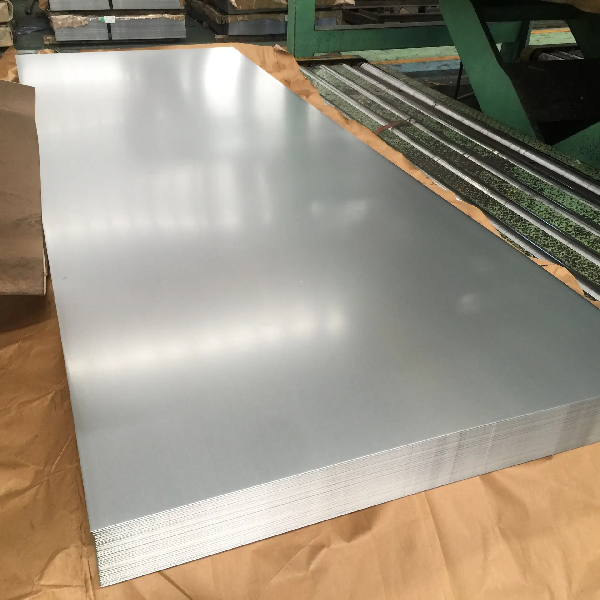
In the basic buying and selling of galvanized sheets, cold rolling is mainly dominated by hot galvanizing, and hot rolled substrates are very rare. So, what is the difference between hot rolled substrates and cold rolled substrates in terms of hot-dip galvanized products? Let’s briefly explain the following areas:
1. Cost fee
Due to the lack of one process flow compared to cold-rolled substrates, hot-dip galvanizing of substrates is more cost-effective than cold-rolled manufacturing, mainly in terms of quenching cost and cold, cold rolling, and cost. Other process flows are similar to the two.
2. Quality characteristics
Due to the fact that the hot-rolled substrate only undergoes acid pickling, passivation, and quenching to eliminate surface residues, its surface is relatively unsmooth, and the zinc layer has good adhesion. The coating thickness is heavier than 140/140g/m2. But the thickness specifications do not have the high precision of cold rolling, as most of them are thick zinc layers, and the thickness control of the zinc layer is uneven. There is not much difference in physical properties, and even some performance improvements are better in cold rolling
3. Main purpose
Hot rolled galvanized sheet is often used for structural prefabricated components with low surface specifications but high compressive strength thickness specifications due to its lower dimensional precision and surface quality compared to cold rolled galvanized sheet.
For example, components of household appliances such as fully automatic washing machines and refrigerators, automotive internal components, chassis components, passenger car compartments, cast-in-place slabs, highway guardrails, cold drawn steel sections, etc.
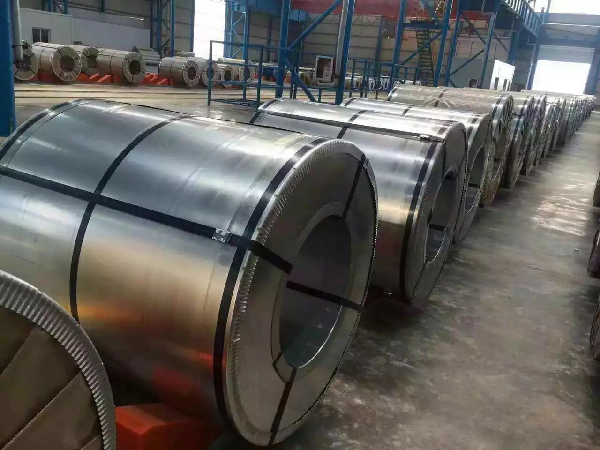

Due to the low cost of hot-rolled galvanized sheet and technological progress, the thickness of specifications and models is also increasing, and the demand is also gradually increasing.
Post time: Aug-14-2023